| Molecular Weight: | 380.16 |
| Volume: | 394.998 |
| LogP: | 5.773 |
| LogD: | 3.427 |
| LogS: | -3.688 |
| # Rotatable Bonds: | 2 |
| TPSA: | 90.9 |
| # H-Bond Aceptor: | 5 |
| # H-Bond Donor: | 3 |
| # Rings: | 4 |
| # Heavy Atoms: | 5 |
| QED Drug-Likeness Score: | 0.422 |
| Synthetic Accessibility Score: | 3.875 |
| Fsp3: | 0.348 |
| Lipinski Rule-of-5: | Accepted |
| Pfizer Rule: | Accepted |
| GSK Rule: | Rejected |
| BMS Rule: | 0 |
| Golden Triangle Rule: | Accepted |
| Chelating Alert: | 0 |
| PAINS Alert: | 0 |
| Caco-2 Permeability: | -4.836 |
| MDCK Permeability: | 1.5203277143882588e-05 |
| Pgp-inhibitor: | 0.204 |
| Pgp-substrate: | 0.984 |
| Human Intestinal Absorption (HIA): | 0.027 |
| 20% Bioavailability (F20%): | 0.119 |
| 30% Bioavailability (F30%): | 0.088 |
| Blood-Brain-Barrier Penetration (BBB): | 0.009 |
| Plasma Protein Binding (PPB): | 96.10962677001953% |
| Volume Distribution (VD): | 0.642 |
| Pgp-substrate: | 7.409558296203613% |
| CYP1A2-inhibitor: | 0.643 |
| CYP1A2-substrate: | 0.721 |
| CYP2C19-inhibitor: | 0.635 |
| CYP2C19-substrate: | 0.134 |
| CYP2C9-inhibitor: | 0.836 |
| CYP2C9-substrate: | 0.965 |
| CYP2D6-inhibitor: | 0.544 |
| CYP2D6-substrate: | 0.376 |
| CYP3A4-inhibitor: | 0.186 |
| CYP3A4-substrate: | 0.162 |
| Clearance (CL): | 4.069 |
| Half-life (T1/2): | 0.146 |
| hERG Blockers: | 0.011 |
| Human Hepatotoxicity (H-HT): | 0.565 |
| Drug-inuced Liver Injury (DILI): | 0.962 |
| AMES Toxicity: | 0.627 |
| Rat Oral Acute Toxicity: | 0.894 |
| Maximum Recommended Daily Dose: | 0.992 |
| Skin Sensitization: | 0.81 |
| Carcinogencity: | 0.713 |
| Eye Corrosion: | 0.005 |
| Eye Irritation: | 0.878 |
| Respiratory Toxicity: | 0.957 |
 Natural Product: NPC319200
Natural Product: NPC319200| Natural Product ID: | NPC319200 |
| Common Name*: | 1,3,5-Trihydroxy-2-(2',2'-Dimethyl-4'-Isopropenyl)Cyclopentanylxanthone |
| IUPAC Name: | 2-[(1S,4S)-2,2-dimethyl-4-prop-1-en-2-ylcyclopentyl]-1,3,5-trihydroxyxanthen-9-one |
| Synonyms: | 6-deoxy-5-O-demethylpaxanthonin |
| Standard InCHIKey: | AUUIZUXRGRVPCU-GXTWGEPZSA-N |
| Standard InCHI: | InChI=1S/C23H24O5/c1-11(2)12-8-14(23(3,4)10-12)18-16(25)9-17-19(21(18)27)20(26)13-6-5-7-15(24)22(13)28-17/h5-7,9,12,14,24-25,27H,1,8,10H2,2-4H3/t12-,14+/m0/s1 |
| SMILES: | CC(=C)[C@H]1C[C@@H](C(C1)(C)C)c1c(O)cc2c(c1O)c(=O)c1c(o2)c(O)ccc1 |
| Synthetic Gene Cluster: | n.a. |
| ChEMBL Identifier: | CHEMBL447199 |
| PubChem CID: |
11245970 |
| Chemical Classification**: |
|
*Note: the InCHIKey will be temporarily assigned as the "Common Name" if no IUPAC name or alternative short name is available.
**Note: the Chemical Classification was calculated by NPClassifier Version 1.5. Reference: PMID:34662515.
 Species Source
Species Source
☑ Note for Reference:
In addition to directly collecting NP source organism data from primary literature (where reference will provided as NCBI PMID or DOI links), NPASS also integrated them from below databases:
☉ UNPD: Universal Natural Products Database [PMID: 23638153].
☉ StreptomeDB: a database of streptomycetes natural products [PMID: 33051671].
☉ TM-MC: a database of medicinal materials and chemical compounds in Northeast Asian traditional medicine [PMID: 26156871].
☉ TCM@Taiwan: a Traditional Chinese Medicine database [PMID: 21253603].
☉ TCMID: a Traditional Chinese Medicine database [PMID: 29106634].
☉ TCMSP: The traditional Chinese medicine systems pharmacology database and analysis platform [PMID: 24735618].
☉ HerDing: a herb recommendation system to treat diseases using genes and chemicals [PMID: 26980517].
☉ MetaboLights: a metabolomics database [PMID: 27010336].
☉ FooDB: a database of constituents, chemistry and biology of food species [www.foodb.ca].
 NP Quantity Composition/Concentration
NP Quantity Composition/Concentration
☑ Note for Reference:
In addition to directly collecting NP quantitative data from primary literature (where reference will provided as NCBI PMID or DOI links), NPASS also integrated NP quantitative records for specific NP domains (e.g., NPS from foods or herbs) from domain-specific databases. These databases include:
☉ DUKE: Dr. Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases.
☉ PHENOL EXPLORER: is the first comprehensive database on polyphenol content in foods [PMID: 24103452], its homepage can be accessed at here.
☉ FooDB: a database of constituents, chemistry and biology of food species [www.foodb.ca].
 Biological Activity
Biological Activity
☑ Note for Activity Records:
☉ The quantitative biological activities were primarily integrated from ChEMBL (Version-30) database and were also directly collected from PubMed literature. PubMed PMID was provided as the reference link for each activity record.
 Chemically structural similarity: I. Similar Active Natural Products in NPASS
Chemically structural similarity: I. Similar Active Natural Products in NPASSTop-200 similar NPs were calculated against the active-NP-set (includes 4,3285 NPs with experimentally-derived bioactivity available in NPASS)
Similarity level is defined by Tanimoto coefficient (Tc) between two molecules. Tc lies between [0, 1] where '1' indicates the highest similarity. What is Tanimoto coefficient 
● The left chart: Distribution of similarity level between NPC319200 and all remaining natural products in the NPASS database.
● The right table: Most similar natural products (Tc>=0.56 or Top200).
 Chemically structural similarity: II. Similar Clinical/Approved Drugs
Chemically structural similarity: II. Similar Clinical/Approved DrugsSimilarity level is defined by Tanimoto coefficient (Tc) between two molecules.
● The left chart: Distribution of similarity level between NPC319200 and all drugs/candidates.
● The right table: Most similar clinical/approved drugs (Tc>=0.56 or Top200).
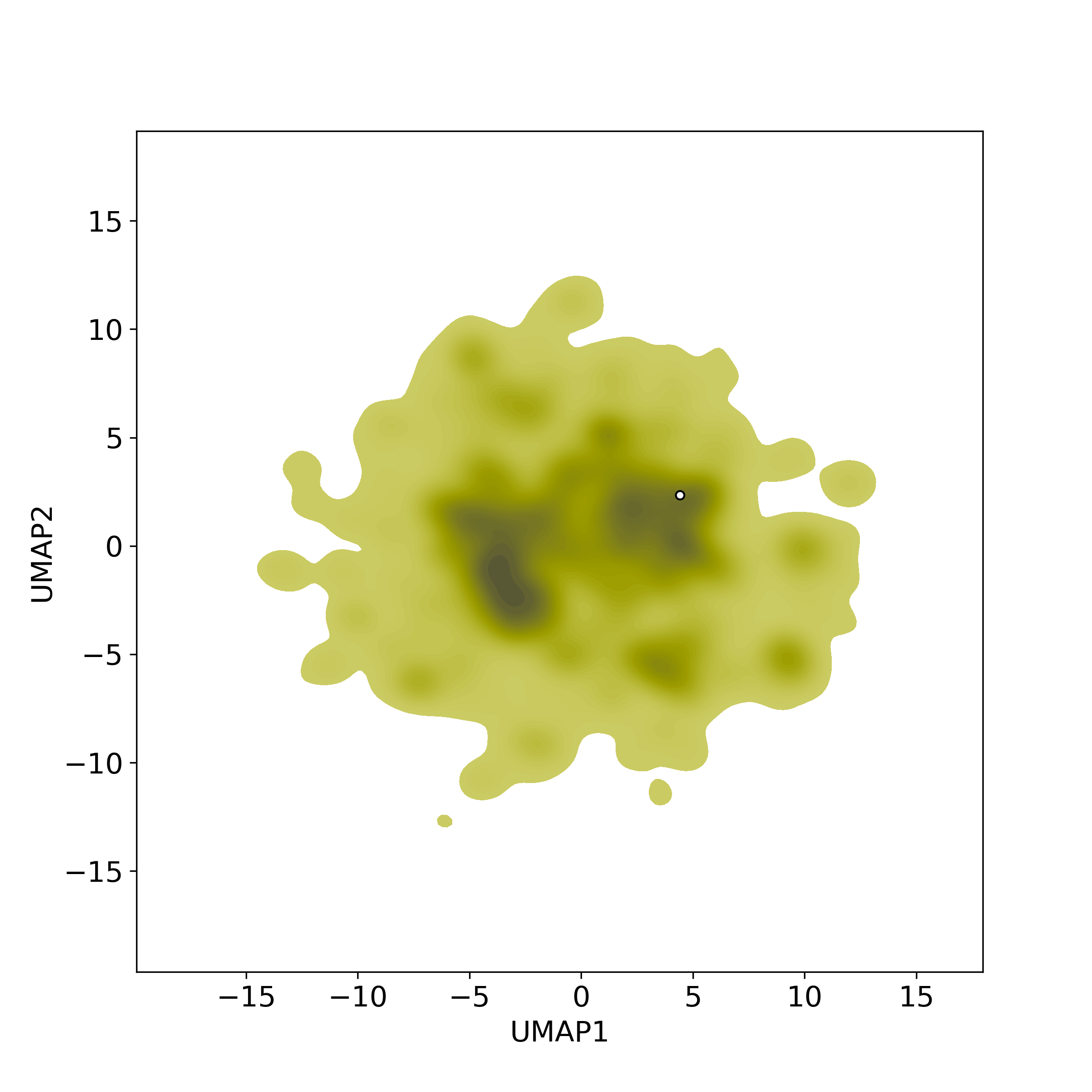
 Bioactivity similarity: Similar Natural Products in NPASS
Bioactivity similarity: Similar Natural Products in NPASSBioactivity similarity was calculated based on bioactivity descriptors of compounds. The bioactivity descriptors were calculated by a recently developed AI algorithm Chemical Checker (CC) [Nature Biotechnology, 38:1087–1096, 2020; Nature Communications, 12:3932, 2021], which evaluated bioactivity similarities at five levels:
☉ A: chemistry similarity;
☉ B: biological targets similarity;
☉ C: networks similarity;
☉ D: cell-based bioactivity similarity;
☉ E: similarity based on clinical data.
Those 5 categories of CC bioactivity descriptors were calculated and then subjected to manifold projection using UMAP algorithm, to project all NPs on a 2-Dimensional space. The current NP was highlighted with a small circle in the 2-D map. Below figures: left-to-right, A-to-E.