Part II. USING MPI
6. Communicators and Processing
Groups in MPI.
Basic Concept
There are well-defined process groups in MPI. The most obvious
examples are the group of all processes, MPI_GROUP_WORLD,
which is defined in the MPI_COMM_WORLD
communicator.
However, often it is more efficient to define subgroups of the world
and associate communicators to perform communications only within these
subgroups.
The following Figure illustrates a user-defined communicator with 4
processors:
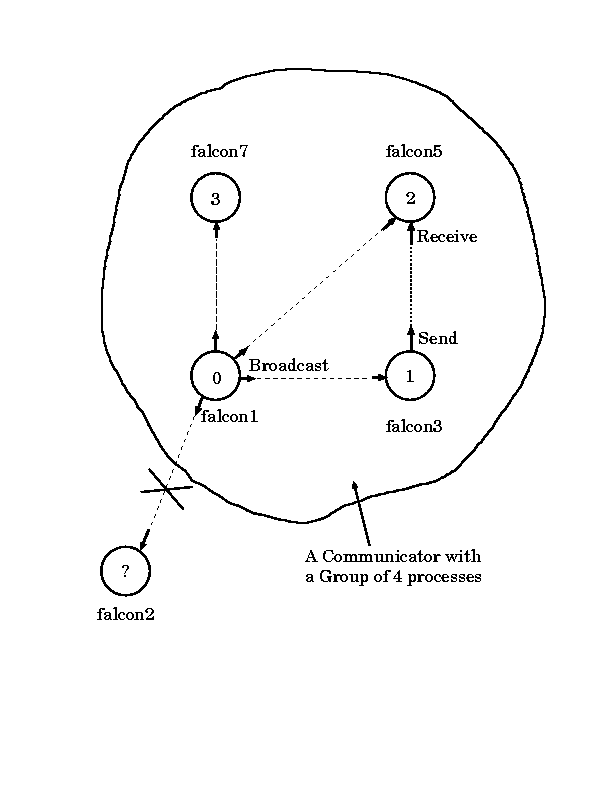
Here, we introduce some MPI group and communicator routines by
an example.
This example shows how to create:
-
a subgroup within the MPI_GROUP_WORLD
-
a subcommunicator in MPI_COMM_WORLD
by using the MPI_Group_excl
and MPI_Comm_create routines.
void *sbuf, *rbuf, sbuf1,
rbuf1;
MPI_Group wcomm,
wgroup, group1;
MPI_Comm subcomm;
static int ranks[]
= {0};
MPI_Init(&argc,
&argv);
MPI_Comm_group(MPI_COMM_WORLD,
&wgroup);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,
&rank);
wcomm = MPI_COMM_WORLD;
MPI_Group_excl(wcomm,
1, ranks, &group1);
MPI_Comm_create(wgroup,
group1, &subcomm);
if(rank != 0)
{
.....
/* compute on nodes within group1 */
MPI_Reduce(sbuf,
rbuf, count, MPI_INT, MPI_SUM, 1, subcomm);
.....
}
MPI_Reduce(sbuf1, rbuf1,
count1, MPI_INT, MPI_SUM, 0, wcomm);
MPI_Comm_free(&subcomm);
MPI_Group_free(&group1);
MPI_Group_free(&wgroup);
MPI_Finalize();
MPI_Comm_group routine
defines the wgroup group
associated with MPI_COMM_WORLD.
MPI_Group_excl routine
excludes the first node in the original group, MPI_GROUP_WORLD, to form
the subgroup group1.
MPI_Comm_create routine
creates a communicator for group1.
After you create the communicator subcomm,
you can perform both point-to-point communication and collective communication
within the subgroup using this communicator, subcomm.
One can also create new groups using:
MPI_Group_incl
MPI_Group_union
MPI_Group_intersection
MPI_Group_difference
MPI_Group_range_incl
MPI_Group_range_excl
You can find out more about these routines from the MPI Standard documentation.
It is a good practice is to free, after completing the operation, the
group and communicator created in the program using the routines MPI_Comm_free
and MPI_Group_free.
Summary of MPI routines (optional reading)
Group Accessors
MPI_Group_size(MPI_Group
group, int *size)
returns number of processes in group
MPI_Group_rank(MPI_Group group,
int *rank)
returns rank of calling process in group
MPI_Group_translate_ranks(MPI_Group
group1, int n, int *ranks1, MPI_Group group2, int *ranks2)
translates ranks of processes in one group to those in another
group
MPI_Group_compare(MPI_Group group1,
MPI_Group group2, int *result)
compares group members and group order
Group Constructors
MPI_Comm_group(MPI_Comm
comm, MPI_Group *group)
returns the group associated with a communicator
MPI_Group_union(MPI_Group group1,
MPI_Group group2, MPI_Group *newgroup)
creates a group by combining two groups
MPI_Group_intersection(MPI_Group
group1, MPI_Group group2,MPI_Group *newgroup)
creates a group from the intersection of two groups
MPI_Group_difference(MPI_Group
group1, MPI_Group group2,MPI_Group *newgroup)
creates a group from the difference between two groups
MPI_Group_incl(MPI_Group group,
int n, int *ranks, MPI_Group *newgroup)
creates a group from listed members of an existing group
MPI_Group_excl(MPI_Group group,
int n, int *ranks, MPI_Group *newgroup)
creates a group excluding listed members of an existing group
MPI_Group_range_incl(MPI_Group
group, int n, int ranges[][3], MPI_Group *newgroup)
creates a group according to first rank, stride, last rank
MPI_Group_range_excl(MPI_Group
group, int n, int ranges[][3], MPI_Group *newgroup)
creates a group by deleting according to first rank, stride,
last rank
Group Destructors
MPI_Group_free(MPI_Group
*group)
marks a group for deallocation
Communicator Accessors
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_Comm
comm, int *size)
returns number of processes in communicator's group
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_Comm comm,
int *rank)
returns rank of calling process in communicator's group
MPI_Comm_compare(MPI_Comm comm1,
MPI_Comm comm2, int *result)
compares two communicators
Communicator Constructors
MPI_Comm_dup(MPI_Comm
comm, MPI_Comm *newcomm)
duplicates a communicator
MPI_Comm_create(MPI_Comm comm,
MPI_Group group, MPI_Comm *newcomm)
creates a new communicator for a group
MPI_Comm_split(MPI_Comm comm,
int color, int key, MPI_Comm *newcomm)
splits a communicator into multiple, non-overlapping communicators
Communicator Destructors
MPI_Comm_free(MPI_Comm
*comm)
marks a communicator for deallocation
A Programing Example: Forest Dynamics Model
Problem
In forest dynamics models, leaf-area profile growth is dictated
by the amount of available light. In some models, diffuse light at a given
grid point depends on data at grid points in cardinal directions (N,E,S,W).
If one views the processors laid out in a 2-dimensional grid, one would
like to exchange data among processors sharing the same row and processors
sharing the same column. This can be accomplished by using groups of processors.
Suppose we have 12 processors laid out in a 3x4 grid, where the number
in the box is the processor number.

Since data must be exchanged among rows and columns of processors, we
must create a group for each row and a group for each column. In our example,
7 different groups must thus be generated. However, a particular processor
will belong to only 2 of these groups -- one row group and one column group.
Programing Steps
It should first be noted that MPI does not provide a mechanism
to build groups from scratch; they can only be developed from previously
defined ones. This leads to an obvious question: How can one build the
first group? You must start with the base group of all processes, which
is associated with the MPI_COMM_WORLD communicator.
Steps:
-
Start with an existing communicator: MPI_COMM_WORLD
-
Access the base group of all processes: MPI_COMM_GROUP( )
-
Create the new group: MPI_GROUP_INCL ( )
-
Create the communicator for the new group: MPI_COMM_CREATE ( )
This last step is essential because all communication events within
the group are activated by a communicator for the group, not by the group
object itself.
Code
c Get base group
call MPI_COMM_GROUP(MPI_COMM_WORLD,bgrp,ierr)
c
c Learn row and column
call MPI_COMM_RANK(MPI_COMM_WORLD,irank,ierr)
irow = MOD(irank,NROW) +
1
icol = INT(irank/NROW) +
1
c
c Build row groups
row_list(1) = 0
do i=2,NCOL
row_list(i)
= row_list(i-1) + NROW
end do
do i=1,NROW
call MPI_GROUP_INCL(bgrp,NCOL,row_list,grp,ierr)
call MPI_COMM_CREATE(MPI_COMM_WORLD,grp,tcomm,ierr)
if (irow
.eq. i) row_comm=tcomm
do j=1,NCOL
row_list(j) = row_list(j)+1
end do
end do
c
c Build column groups
do i=1,NROW
col_list(i) = i-1
end do
do i=1,NCOL
call MPI_GROUP_INCL(base_grp,NROW,col_list,grp,ierr)
call MPI_COMM_CREATE(MPI_COMM_WORLD,grp,temp_comm,ierr)
if (icol .eq. i) col_comm=temp_comm
do j=1,NROW
col_list(j) = col_list(j) + NROW
end do
end do
c
c Collect local maximum heights
call MPI_ALLGATHER(maxht,1,MPI_INTEGER,
1 row_hgt,1,MPI_INTEGER,
row_comm,ierr)
call MPI_ALLGATHER(maxht,1,MPI_INTEGER,
1 col_hgt,1,MPI_INTEGER,col_comm,ierr)
return
end
Homework
7.

